Amblyopia, commonly known as lazy eye, is a vision development disorder that manifests as reduced sight in one eye during childhood. While this is commonly thought of as a crossed eye, many cases of amblyopia are not from obvious causes. Regular eye checkups for children can help detect conditions like amblyopia early.
Vision therapy can help train your eyes by working closely with children to enhance visual skills. Professional vision therapy often involves specialized tools, but many simple exercises can be done at home to help correct lazy eyes! Monocular vision activities, like colouring within the lines, and binocular vision activities, like pencil push-ups or dots-to-dots, can help correct amblyopia.
Understanding How Exercises Help
Amblyopia occurs when one eye or both eyes becomes weaker, leading to reduced vision. Early intervention in children and consistent treatment is important for improving vision and preventing long-term complications. If untreated, amblyopia can persist into adulthood, affecting vision quality and depth perception.
Eye exercises are designed to strengthen the weaker eye(s) and improve coordination between both eyes. These exercises help stimulate the brain’s visual processing areas, encouraging equal use of both eyes. Regular practice can significantly enhance vision and, in some cases, reduce dependency on corrective eyewear.
Incorporating eye exercises into your child’s daily routine can offer multiple benefits, including:
- Improved visual acuity
- Enhanced binocular vision and depth perception
- Reduced eye strain and discomfort
- Increased confidence and quality of life
Lazy Eye Exercises
Exercises and activities to help improve vision are either done monocularly (with just one eye, using a patch to cover the other eye) or binocularly (with both eyes). Monocular vision activities focus on training the a weak eye while binocular vision activities train both eyes to better work together.
Monocular Vision Activity Examples
Colouring Within The Lines
- Give your child a colouring book with simple pictures and well-defined lines.
- Ensure their crayons or pencil crayons are sharp.
- Have them carefully colour the pictures, staying within the lines.
- Supervise (or colour with them!) to make sure they keep the patch on.
General Patch Therapy
Rather than having your child do a prescribed activity, you can utilize a patch with some of the things they already love doing. That way, the weaker eye will get more practice outside of what your child might consider “boring”. You know your child’s interests best, but you can consider:
- Playing with handheld toys
- Reading books
- Jigsaw puzzles
- (Age-appropriate) word games like boggle, crosswords, or sudoku
- Handheld video games where appropriate
Start with short 30-minute sessions and gradually increase the duration, keeping track of their improvement as you do so.
Binocular Vision Activity Examples
Brock String Exercise
- Use a Brock String (a white string with several coloured beads around 15 feet long)
- Hold the string so that one end is attached to a fixed point (like a doorknob) and the other end is at your nose
- Focus on each bead sequentially. If your eyes are aligned, you should see two strings in an X-shape with the bead in the middle
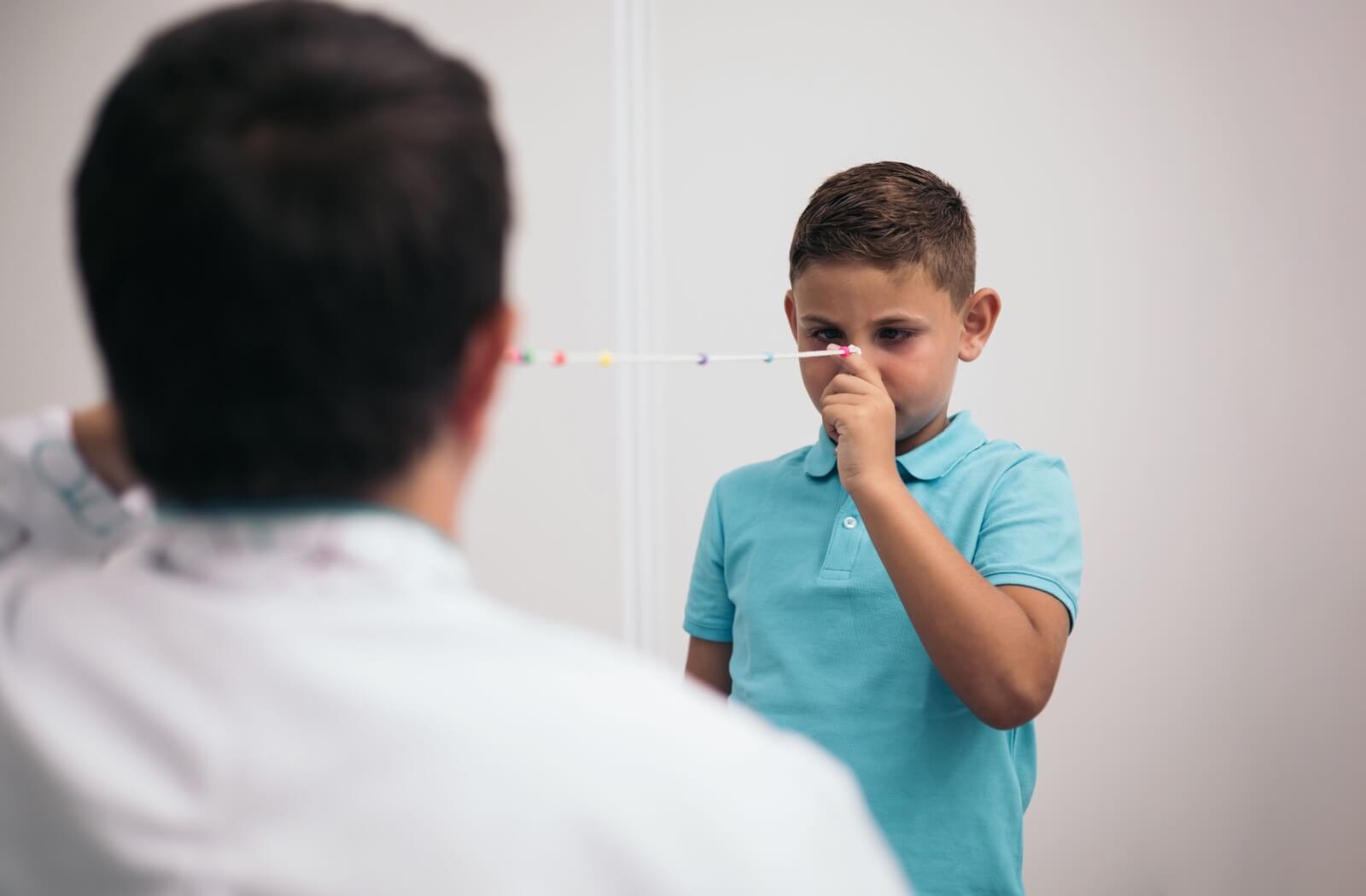

Pencil Push-Ups
- Hold a pencil in front of you at arm’s length, at eye level.
- Keep both eyes focused on the pencil. If the pencil has a visual element like a number or letter, focus on that.
- Slowly move the pencil closer to your nose without it becoming blurry or doubled
- Once the pencil becomes blurry, move it back.
- Try for 5-10 repetitions per session (at least 1-3 times per day), gradually increasing repetitions as vision improves.
Dots-to-Dots
- Draw a line of dots on a rectangular card. Stock paper or cardboard work well.
- Hold the card lengthwise. Touch it to your nose so the line of dots is perpendicular to your face.
- Tilt the card down slightly and focus on the farthest dot, which should be singular and not blurry.
- If your eyes are working together, the line of dots will look like they’re in an A-shape. Hold for a count of five.
- Focus on the next dot. If your eyes continue working together, the line of dots will look like they’re in an X-shape.
- Maintain the X-shape for five seconds before proceeding to the next dot.
- At the closest dot, the line of dots should appear as though in a V-shape
Other Treatments for Lazy Eye
While at-home exercises for lazy eyes can help improve visual skills, it can take several weeks to months to strengthen vision in the weaker eye.
Your optometrist can help best guide you for treatments that will suit your unique eye needs, but other forms of treatments for amblyopia include:
- Vision Therapy: Overseen by your Optometrist in-office, which includes techniques like prism lenses, optical filters, and computer software
- Corrective Eyeglasses or Contact Lenses: Prescriptions can address the needs of each eye and work to strengthen vision in the weaker eye
- Eye Drops: Used to blur the vision of the stronger eye with a medication (Isopto Atropine) so the weaker eye is forced to pick up the slack
- Surgery: An option that may be recommended when either other treatments have not been effective, or if your lazy eye is caused by a droopy eyelid, cataract, or squint
Take the Next Step
Lazy eye exercises for amblyopia can be highly effective, especially when started early. While there is evidence that vision therapy can be effective at any age, it is generally much simpler and less intense at a young age. This makes early detection paramount.
The Optometrists at Olds Eyecare, Sundre Eyecare, Bonavista Eyecare and Carstairs Eyecare specialize in how we can use up-to-date technology to support you and your family’s eye health, investing in your long-term vision. If you or your child has amblyopia, contact us today to see how we can best help you with vision therapy.